

Make sure you train the entire MARCH mnemonic until it becomes second nature. But remember-training only to place tourniquets is simply not enough. When you see such signs, apply a tourniquet, positioning it high and tight on the injured limb.

Massive hemorrhage must be assessed and addressed rapidly and thoroughly before moving on to the next step. More readily treated in the field, through the use of tourniquets, hemostatic gauze, pressure bandages, and junctional devices.More common than any other life-threatening emergency on the battlefield.TCCC dict ates that massive hemorrhage is the first treatment priority in battlefield trauma for several reasons, as it is: The real work of tactical field care begins with an assessment: In this blog, we will focus on the second phase-the Tactical Field Care (TFC) phase. Most additional interventions during this phase of care are similar to those performed during normal EMS operations. However, major emphasis is placed on the reassessment of interventions and hypothermia management. Tactical Evacuation Care (TACEVAC) phase: During this phase of care, an effort is made to move the casualty toward a definitive treatment facility.In this phase, assessment and treatment priorities focus on the preventable causes of death as defined by military medical evidence: Major Hemorrhage, Airway, Breathing/Respirations, Circulation, and Head & Hypothermia. Tactical Field Care (TFC) phase: This phase can be initiated once the threat has been addressed and/or the casualty is in a safe location.Care Under Fire (CUF) phase: Wherein the primary concern is any threat to life/safety in the form of enemy fire or environment, as well as utilizing tourniquets to manage massive hemorrhage.The evidence-based approach that motivated the Committee on Tactical Combat Casualty Care (CoTCCC) to adopt the M A R C H mnemonic has drastically changed that approach for the better.Īccording to the TCCC guidelines, there are three phases of care: The old school approach to trauma was: Airway, Breathing, Circulation (ABC). Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) revolutionized our approach to trauma by utilizing evidence-based medicine in replacing the antiquated ABCs with the MARCH mnemonic. If you are not familiar with MARCH, here is what you need to know. Such an increase in acidity damages the tissues and organs of the body and can reduce myocardial performance, further reducing the oxygen delivery.Stop the Bleed > MARCH Mnemonic and TCCC MARCH Mnemonic and TCCC Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) revolutionized our approach to trauma by utilizing evidence-based medicine in replacing the antiquated “ABCs” with the MARCH mnemonic. In the absence of blood-bound oxygen and nutrients ( hypoperfusion), the body's cells burn glucose anaerobically for energy, causing the release of lactic acid, ketone bodies, and other acidic compounds into the blood stream, which lower the blood's pH, leading to metabolic acidosis. This in turn can halt the coagulation cascade, preventing blood from clotting. Severe haemorrhage in trauma diminishes oxygen delivery, and may lead to hypothermia.
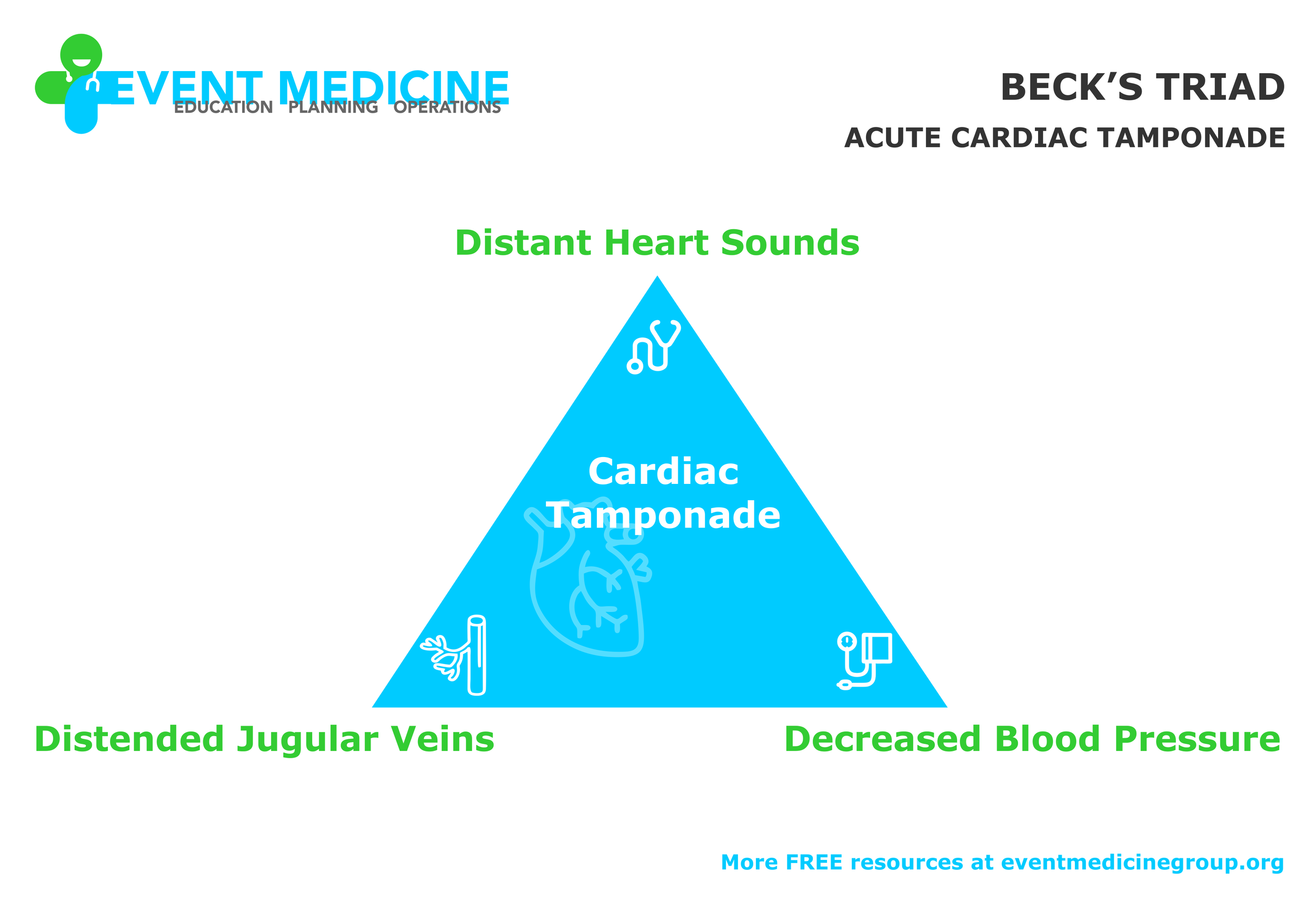
The three conditions share a complex relationship each factor can compound the others, resulting in high mortality if the cycle continues uninterrupted. Commonly when someone presents with these signs damage control surgery is employed to reverse the effects. This combination is commonly seen in patients who have sustained severe traumatic injuries and results in a significant rise in the mortality rate. The trauma triad of death is a medical term describing the combination of hypothermia, acidosis and coagulopathy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
